This post describes the CPython implementation of the list object. CPython is the most used Python implementation.
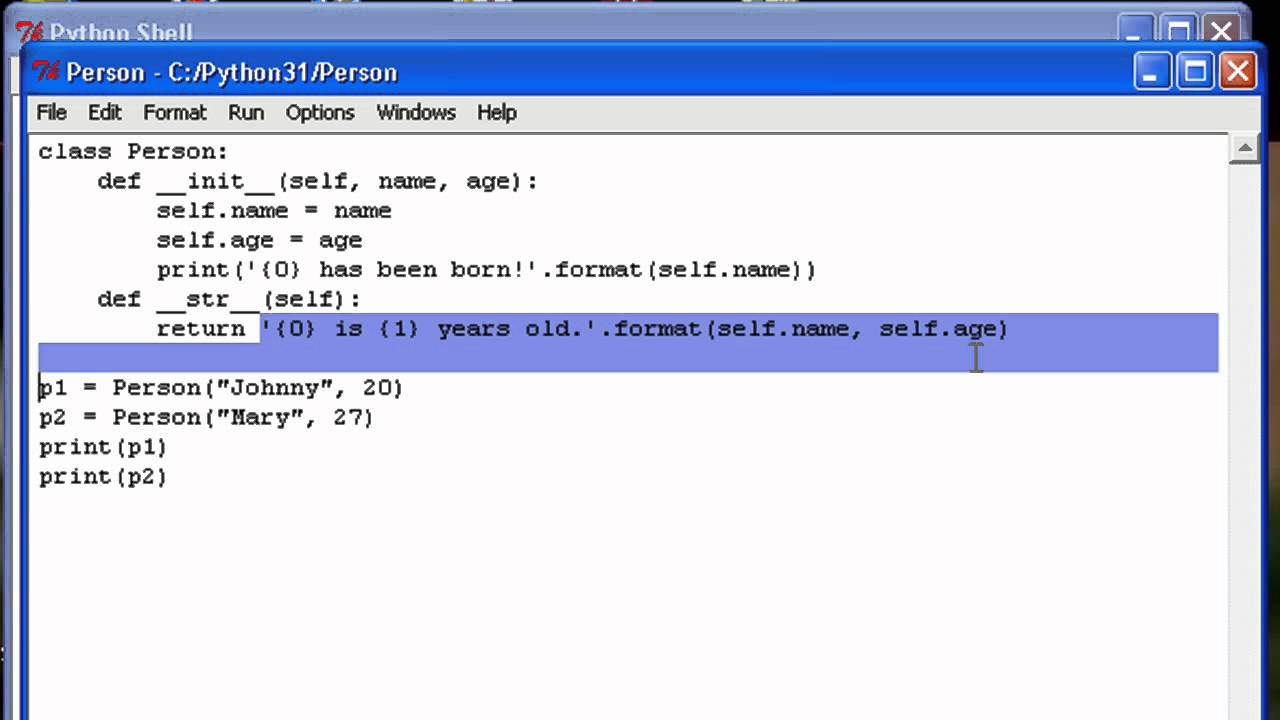
Python Classes And Objects Python 3 Class and Objects Tutorial For Beginners 2019. Here in this blog post Coding compiler sharing a tutorial on Python 3 classes and objects for beginners. This Python tutorial is for beginners and intermediate learners who are looking to master in Python programming. Objects, values and types¶. Objects are Python’s abstraction for data. All data in a Python program is represented by objects or by relations between objects. (In a sense, and in conformance to Von Neumann’s model of a “stored program computer”, code is also represented by objects.). Python老鸟都应该看过那篇非常有吸引力的 Saving 9 GB of RAM with Python’s slots 文章,作者使用了slots让内存占用从25.5GB降到了16.2GB。在当时来说,这相当于用一个非常简单的方式就降低了30%的内存.
On the class-level, each slot has as a descriptor that knows its unique position in the instance list. There is a good explanation of how it works by Raymond Hettinger. Although it was written 10 years ago, the concept stays the same. Bonus: function attributes. Python's dictionary is so fundamental to Python, that many other objects using it too.

Lists in Python are powerful and it is interesting to see how they are implemented internally.
Following is a simple Python script appending some integers to a list and printing them.
As you can see, lists are iterable.
List object C structure
A list object in CPython is represented by the following C structure. ob_item is a list of pointers to the list elements. allocated is the number of slots allocated in memory.
List initialization

Let’s look at what happens when we initialize an empty list. e.g. l = [].

It is important to notice the difference between allocated slots and the size of the list. The size of a list is the same as len(l). The number of allocated slots is what has been allocated in memory. Often, you will see that allocated can be greater than size. This is to avoid needing calling realloc each time a new elements is appended to the list. We will see more about that later.
Append
We append an integer to the list: l.append(1). What happens? The internal C function app1() is called:
Let’s look at list_resize(). It over-allocates memory to avoid calling list_resize too many time. The growth pattern of the list is: 0, 4, 8, 16, 25, 35, 46, 58, 72, 88, …
4 slots are now allocated to contain elements and the first one is the integer 1. You can see on the following diagram that l[0] points to the integer object that we just appended. The dashed squares represent the slots allocated but not used yet.
Append operation amortized complexity is O(1).
We continue by adding one more element: l.append(2). list_resize is called with n+1 = 2 but because the allocated size is 4, there is no need to allocate more memory. Same thing happens when we add 2 more integers: l.append(3), l.append(4). The following diagram shows what we have so far.
Insert
Let’s insert a new integer (5) at position 1: l.insert(1,5) and look at what happens internally. ins1() is called:
The dashed squares represent the slots allocated but not used yet. Here, 8 slots are allocated but the size or length of the list is only 5.
Insert operation complexity is O(n).
Pop
When you pop the last element: l.pop(), listpop() is called. list_resize is called inside listpop() and if the new size is less than half of the allocated size then the list is shrunk.
Pop operation complexity is O(1).
You can observe that slot 4 still points to the integer but the important thing is the size of the list which is now 4.
Let’s pop one more element. In list_resize(), size – 1 = 4 – 1 = 3 is less than half of the allocated slots so the list is shrunk to 6 slots and the new size of the list is now 3.
You can observe that slot 3 and 4 still point to some integers but the important thing is the size of the list which is now 3.
Remove

Python 3 Class Slots Games
Python list object has a method to remove a specific element: l.remove(5). listremove() is called.
To slice the list and remove the element, list_ass_slice() is called and it is interesting to see how it works. Here, low offset is 1 and high offset is 2 as we are removing the element 5 at position 1.
Python 3 Class Tutorial
Remove operation complexity is O(n).
Python 3 Class Property
That’s it for now. I hope you enjoyed the article. Please write a comment if you have any feedback. If you need help with a project written in Python or with building a new web service, I am available as a freelancer: LinkedIn profile. Follow me on Twitter @laurentluce.
